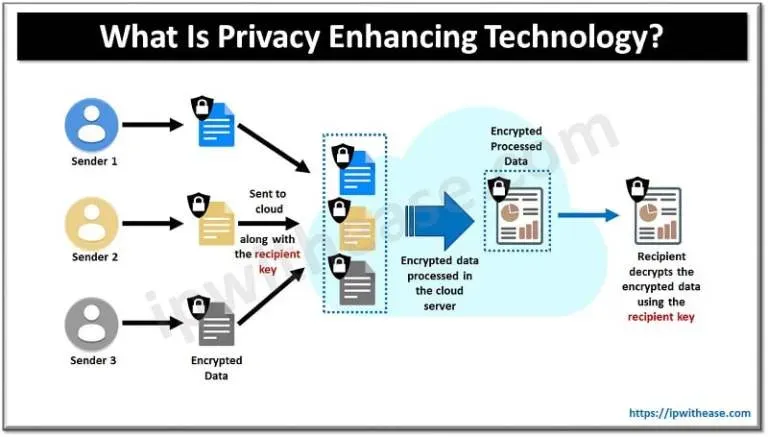
Technology and Data Privacy are shaping today’s digital landscape as organizations race to innovate with AI, cloud services, and connected devices worldwide. Protecting user data while delivering value is no mere compliance chore but a strategic differentiator that can win customers, investors, and regulators. A strong foundation in data governance defines data ownership, access controls, and lifecycle management, aligning privacy with business goals. By integrating privacy into product development, teams minimize data collection, enforce purpose limitation, and boost transparency across products and platforms. This introductory overview sets the stage for practical, scalable strategies that balance risk and opportunity for organizations of any size.
Looking beyond the term privacy, a privacy-preserving approach emphasizes information protection, data minimization, and clear data flows across systems. In this lens, terms like data protection, secure architectures, and consent management become practical design criteria that support trustworthy analytics. Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) suggests weaving related concepts such as data stewardship, governance transparency, and regulatory awareness into content to improve search relevance. Emerging techniques—differential privacy, federated learning, and on-device processing—show how insights can be gained without exposing individual identities. When organizations document data flows, assess risks, and maintain verifiable controls, they create a foundation for innovation that respects user rights.
Technology and Data Privacy: Balancing Innovation with Trust
Technology and Data Privacy are two driving forces shaping today’s digital landscape. As organizations adopt AI, cloud services, and connected devices, protecting user data becomes not just a compliance obligation but a strategic differentiator. Companies that treat privacy as an afterthought risk eroding customer trust and inviting regulatory scrutiny in a fast-evolving environment.
Viewed through the lens of privacy by design, innovation and privacy are not mutually exclusive. Embedding privacy considerations early—through data minimization, purpose limitation, and consent management—helps unlock value while reducing risk. This approach also reinforces data governance and data security, aligning product goals with regulatory expectations and building durable customer trust.
Privacy by Design: Making Privacy a Foundational Principle
Privacy by design should be a foundational principle: embed privacy in every stage of the product lifecycle from ideation to deployment and beyond. By treating privacy as a core requirement, teams can anticipate risks and design controls before they become costly changes.
Concrete practices include data minimization, clear purpose specification, consent management, and the use of privacy-enhancing technologies such as pseudonymization and encryption. Transparent user controls and data portability options further strengthen customer trust while aligning with data governance and regulatory compliance obligations.
Data Governance and Data Security: Structuring Responsibility and Protection
Data governance provides the framework for how data is managed across the organization. Establishing data ownership, cataloging, quality standards, and lifecycle policies creates accountability and clarity, reducing both privacy risk and operational friction. When data governance is strong, data-driven features can scale with confidence.
Coupled with robust data security measures—encryption, secure coding, access controls, and continuous monitoring—data remains protected at rest and in transit. This combination supports compliant operations, speeds incident response, and preserves customer trust through consistent data handling and auditing capabilities.
Regulatory Compliance and Trust: Meeting Requirements While Building Confidence
Regulatory requirements such as GDPR and CCPA shape how organizations collect, store, and process personal data. Compliance should be viewed as a risk-management discipline that signals to customers and partners that privacy is prioritized, not merely checked off as a box.
Practical steps include DPIAs for high-risk processing, transparent data practices, cross-border transfer safeguards, and regular audits. Vendor privacy due diligence and ongoing third-party assessments further strengthen the program and reinforce customer trust while enabling scalable innovation.
The Path Forward: Privacy-Preserving Innovation and Trust as a Core Value
As technology evolves, privacy-preserving techniques enable advanced analytics and AI without exposing personal data. Differential privacy and data anonymization allow insights at scale while minimizing identifiability, creating a governance-friendly data ecosystem.
Approaches such as federated learning and on-device processing reduce centralized data collection, while ethical AI governance—bias monitoring, explainability, and user-centric privacy controls—ensures responsible innovation. Coupled with continuous improvement of data governance, consent practices, and regulatory compliance, organizations can pursue ambitious innovation while preserving customer trust.
Culture, Leadership, and Operational Readiness for Privacy-Driven Innovation
Balancing innovation with trust is as much about culture as technology. Leadership must model privacy-first decision making, invest in privacy and security talent, and reward teams that deliver responsibly. A privacy-centric culture accelerates adoption and reduces risk across the organization by aligning incentives with compliant outcomes.
Operational readiness requires scalable privacy controls, mature incident response, and ongoing training that embeds privacy by design into daily workflows. When privacy becomes a shared value across product, engineering, legal, and security, it emerges as a competitive differentiator that sustains long-term growth and customer trust.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does privacy by design influence data governance and data security in technology products?
Privacy by design embeds privacy into every phase of a product’s lifecycle, driving data minimization, purpose limitation, and consent management. It aligns with data governance and strengthens data security through practices like encryption and access controls, reducing risk and supporting regulatory readiness while enhancing customer trust.
What is data governance and how does it impact regulatory compliance and customer trust in technology platforms?
Data governance defines data ownership, quality standards, and lifecycle policies. When implemented well, it supports regulatory compliance by ensuring proper data handling, retention, and documentation, and it builds customer trust through transparent data practices and accountable stewardship.
Why is data security essential for regulatory compliance and maintaining customer trust in digital services?
Data security safeguards information in transit and at rest using encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring. Strong data security is a cornerstone of regulatory compliance and demonstrates reliability, which in turn reinforces customer trust.
How can organizations implement privacy by design to balance innovation with data governance?
Start with privacy by design from the outset: involve cross-functional teams, conduct DPIAs for high-risk processing, minimize data collection, define retention periods, obtain appropriate consent, and ensure transparency. Align these privacy practices with data governance to enable secure, innovative features.
What role does regulatory compliance play in building customer trust when handling personal data?
Regulatory compliance signals a serious commitment to protecting personal data. It fosters transparent data practices, breach readiness, and third-party due diligence, all of which strengthen customer trust and support responsible innovation.
What practical privacy-preserving techniques support data security and compliance without hampering innovation?
Techniques such as differential privacy, federated learning, and on-device processing enable analytics and AI while reducing data exposure. When paired with robust data governance, encryption, and consent controls, they help maintain regulatory compliance and protect customer trust.
| Key Theme | Core Points | What this Means |
|---|---|---|
| The Landscape: Innovation, Data, and Trust | Technology and Data Privacy are interdependent; innovation provides capabilities while privacy protects trust; privacy should be a design criterion embedded early | Organizations should align product goals with privacy objectives to avoid trust erosion and regulatory risk |
| Privacy by Design | Data minimization; Purpose limitation and consent management; Privacy-enhancing technologies; Transparency and user control; cross-functional collaboration | Privacy becomes a foundational principle across the product lifecycle |
| Data Governance and Data Security | Data ownership, cataloging, and lifecycle; Access controls and monitoring; Encryption and secure coding; Incident response | Balanced governance and security reduce risk while enabling data-driven innovation |
| Regulatory Compliance and Trust | GDPR, CCPA; DPIAs; transparency; cross-border safeguards; audits and third-party due diligence | Compliance signals responsibility and strengthens customer trust |
| The Path Forward: Privacy-Preserving Innovation | Differential privacy, Federated learning, Ethical AI governance, Continuous improvement | Tech progress can continue without compromising privacy by adopting privacy-enhancing strategies |
| Case Studies | Company A: privacy as a post-launch feature; slower adoption; trust erosion. Company B: privacy by design from the outset; better risk management and trust | Illustrates practical benefits of proactive privacy governance |
| Culture, Leadership, and Operational Readiness | Privacy-first leadership; talent investment; scalable privacy controls; ongoing training | Privacy becomes a competitive differentiator through organizational alignment |
Summary
Technology and Data Privacy are central to modern, responsible innovation. In this era, organizations must embrace privacy by design, strengthen data governance and data security, and prioritize regulatory compliance and transparency to unlock the full value of data-driven innovation while earning and maintaining customer trust. By weaving privacy into strategy, governance, and day-to-day product decisions, companies can foster a culture that respects user rights and accelerates trustworthy technology adoption, ensuring sustainable growth in a landscape where innovation and trust reinforce each other.